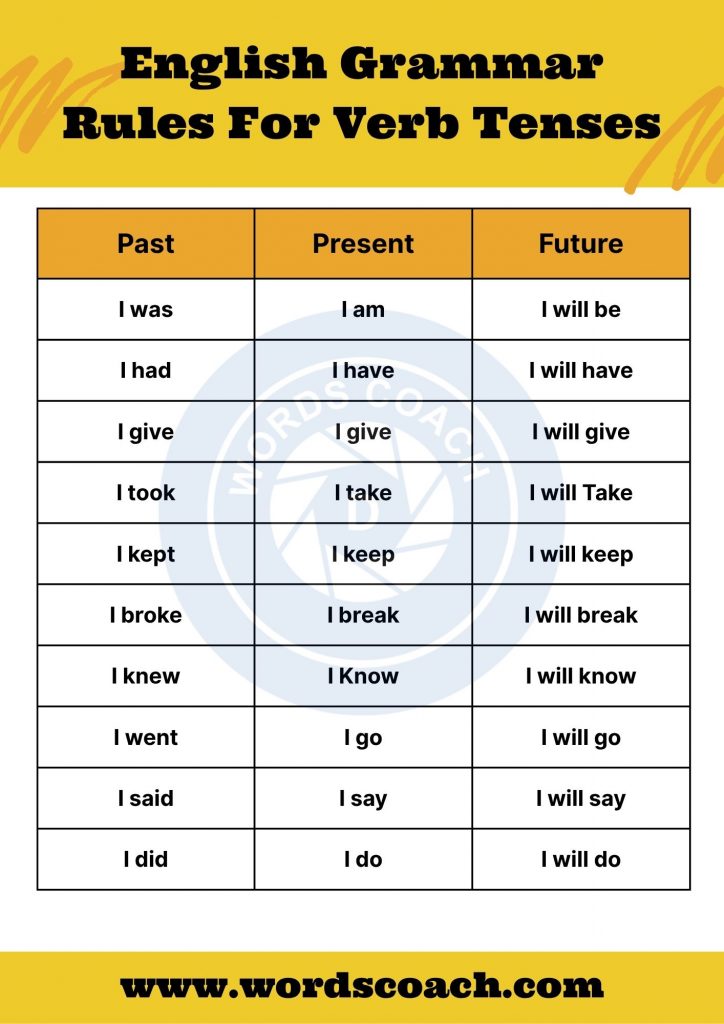
English Verb Tenses
Before we get started with the tenses let’s recall the definition of the verb.
What is a verb? A verb is a word that denotes an action or a state of being. Verb tenses are usually referred to in three main time frames: Past, Present, and Future. Moreover, they further classified into four aspects: Simple, Continuous, Perfect, and Perfect Continuous. With that, we are providing 12 Basic Verb Tenses with Examples for you to understand it more clearly. Tense as a grammatical term expresses time. The meaning of the sentence will be clear only if the right tense is utilized. Let’s dive deep into it.

Tenses Exercises
1. Simple Present Tense:
Simple present tense conveys action in the present. It is applied to show a habitual action or general truth. Predominantly, we use the present tense to describe an action occurring in the present time.
For instance,
I cook every day.
The sun rises in the east.2. Present Continuous Tense:
Present continuous tense is used to delineate an action that is taking place at the current time of speaking. It is also used to depict something that we have arranged to do in the future. The structure of this tense is is/am/are + main verb + ing.
For example,
The boys are playing cricket on the ground.
The train is going to arrive at 6:00 tomorrow morning.
3. Present Perfect Tense:
Present perfect tense is used when we have to describe an action that has been completed in the immediate past or that occurred at an indefinite time in the past, or that began in the past but continues in the present. The structure of this tense is has/have + main verb + ed or en.
For instance,
Have you ever been to Europe?
Gujarat has been a state since 1960.
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
Present perfect continuous tense depicts an action that started in the past, is continuing at present, and may continue in the future. The structure of this tense is has/have + been + main verb + ing.
For example,
It has been raining for the past two days.
She has been watching TV for the last four hours.
5. Simple Past Tense:
Simple past tense refers to an action that was done in the past. Use this tense to show an event or action that took place at a specific time in the past and now it’s over.
For example,
I worked in the IT sector.
The milk used to cost 10 rupees per liter some years ago.
6. Past Continuous Tense:
Past continuous tense describes in progress action in the past when another past action takes place. The structure of this tense is was/were + main verb + ing.
For instance,
Alex was playing video games when his mother arrived home.
Seema was waiting at the airport when her brother got off the plane.
7. Past Perfect Tense:
Past perfect tense refers to an action that leads up to another in the past. The more contemporary past event is expressed in the simple past, and the earlier past event is expressed in the past perfect. The structure of this tense is had + main verb + ed or en.
For example,
Richard had lived in Europe, before he moved to Australia.
He had visited his sister before he went for the study in the USA.
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
Past perfect continuous tense describes an ongoing action in the past that is completed before another action takes place in the past. The structure of this tense is had + been + main verb + ing.
For instance,
She had been studying all day.
Lily had been working in Google for three years when she lost her job.
9. Simple Future Tense:
Simple future tense refers to an action that will take place in the future. Generally, it is used to describe a prediction or intention.
For example,
I am going to move to the USA to pursue my masters.
She will help me tomorrow to complete my assignments.
10. Future Continuous Tense:
Future continuous tense describes an action that is taking place in the present and will continue taking place in the future also. The structure of this tense is will be/shall be + main verb + ing.
For instance,
I will be studying tomorrow.
We shall not be watching a movie today.
11. Future Perfect Tense:
Future perfect tense is used to describe an action that precedes another in the future. The structure of this tense is will/shall + have + main verb + ed or en.
For instance,
By the end of this year, the president will have established new industries in the country.
They will have finished their work by tomorrow.
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
Future perfect continuous tense refers to an ongoing action that will take place prior to a certain time in the future. The structure of this tense is will have + been + main verb + ing.
For example,
I will not have been staying in India by next year.
He will have been dancing for two hours.
To deduce, these are the 12 Basic Verb Tenses with Examples we all should have knowledge about. We can memorize those by using the structure or form of the tenses given above. It will be handy while you are working with the Analytical Writing (AWA) section in the GRE exam or in any kind of general English test.
Read in details for tense Here
Hope it helps!! Happy Learning
Written by,
Jaini Bhavsar (There’s always room for bliss.)
23rd May 2020
Connect with me on LinkedIn
Download the Word Coach Application

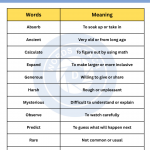

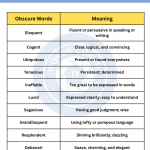


Master this chapter, before proceeding to the next one
Some genuinely nice stuff on this site, I love it.