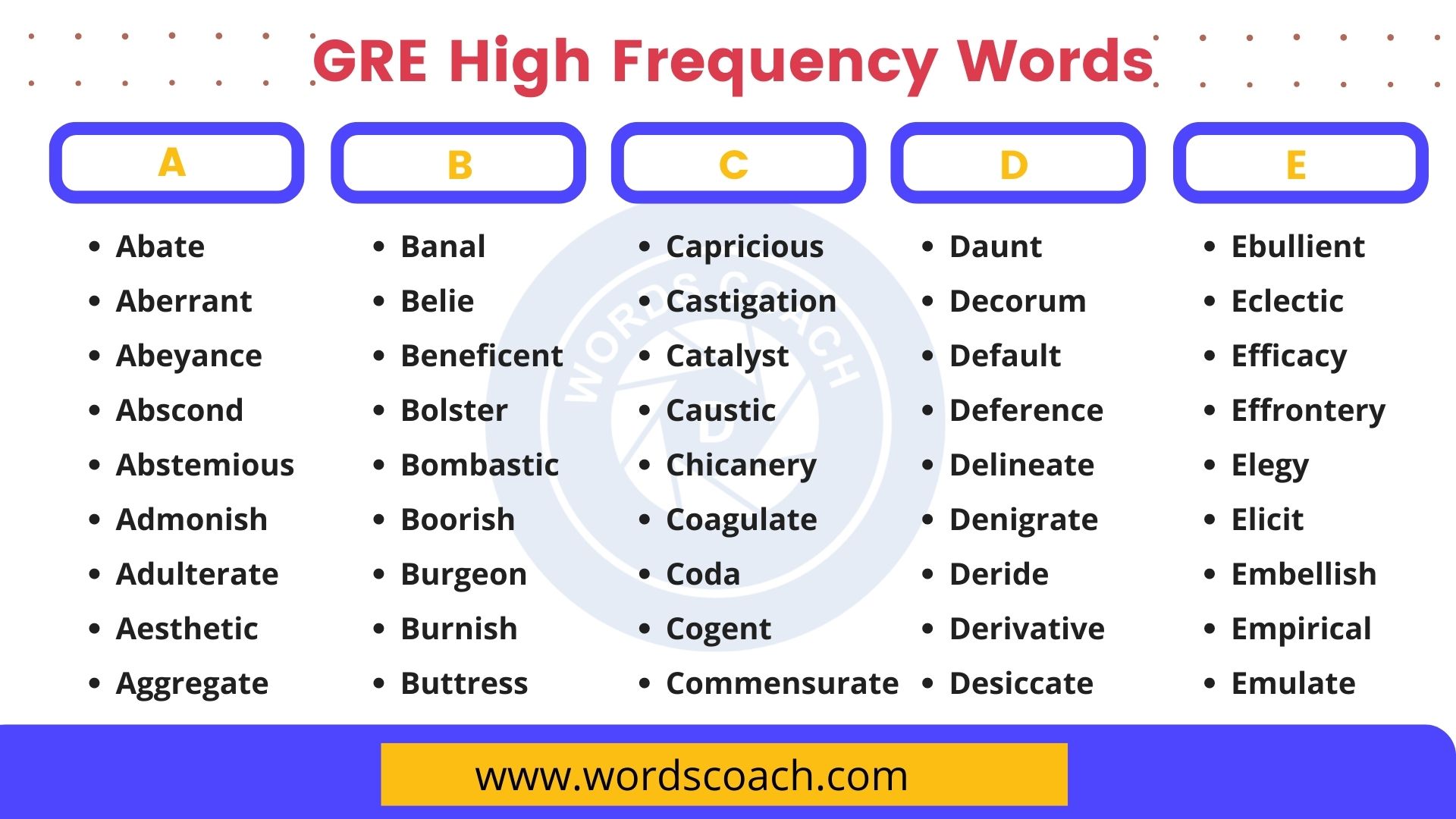
GMAT Vocabulary List
The GMAT can feel like a vocabulary gauntlet, but here’s the secret: it’s not about memorizing obscure words! This blog post equips you with effective strategies to conquer the GMAT Verbal section, focusing on the vocabulary that truly matters.
List of GMAT Vocabulary
- Abate
- Aberrant
- Abjure
- Abscond
- Abstain
- Abyss
- Adulterate
- Advocate
- Aesthetic
- Alacrity
- Ameliorate
- Anachronism
- Antipathy
- Antithetical
- Apathy
- Apocryphal
- Arduous
- Assuage
- Attenuate
- Austere
- Avarice
- Banal
- Bolster
- Bombastic
- Cacophony
- Candid
- Capricious
- Castigate
- Catalyst
- Caustic
- Chicanery
- Cogent
- Contentious
- Contrite
- Convoluted
- Craven
- Decorum
- Deference
- Deride
- Desiccate
- Desultory
- Diatribe
- Diffident
- Dilatory
- Dilettante
- Dirge
- Disabuse
- Disparate
- Dissemble
- Dissonance
- Dogmatic
- Dupe
- Eclectic
- Efficacy
- Elegy
- Eloquent
- Emulate
- Enervate
- Engender
- Ephemeral
- Equivocate
- Erudite
- Esoteric
- Eulogy
- Euphemism
- Exacerbate
- Exculpate
- Exigent
- Exonerate
- Facetious
- Fervid
- Florid
- Foment
- Frugality
- Garrulous
- Gregarious
- Guile
- Harangue
- Homogenous
- Iconoclast
- Imperturbable
- Implacable
- Inchoate
- Ingenious
- Inimical
- Innocuous
- Insipid
- Intransigent
- Intrepid
- Inundate
- Irascible
- Laconic
- Lament
- Lethargic
- Loquacious
- Lucid
- Magnanimous
- Malleable
- Misanthrope
- Mitigate
- Obdurate
- Obfuscate
- Obsequious
- Occlude
- Opprobrium
- Paradox
- Paragon
- Pedant
- Perfidious
- Perfunctory
- Permeate
- Placate
- Plastic
- Plethora
- Pragmatic
- Precipitate
- Prevaricate
- Proclivity
- Prodigal
- Propitiate
- Propriety
- Quotidian
- Repudiate
- Reticent
- Soporific
- Specious
- Spurious
- Stolid
- Sublime
- Tacit
- Taciturn
- Tirade
- Torpid
- Tortuous
GMAT Vocabulary with meaning and example:
Here is a list of GMAT vocabulary words along with their meanings and examples:
- Abate (verb)
- Meaning: To lessen in intensity or degree.
- Example: The storm finally abated, leaving a clear sky.
- Aberrant (adjective)
- Meaning: Deviating from the norm.
- Example: His aberrant behavior attracted the attention of the authorities.
- Abjure (verb)
- Meaning: To renounce or reject solemnly.
- Example: He abjured his allegiance to the old regime.
- Abscond (verb)
- Meaning: To leave hurriedly and secretly, typically to avoid detection.
- Example: The thief absconded with the stolen jewels.
- Abstain (verb)
- Meaning: To choose not to do something.
- Example: She decided to abstain from alcohol for health reasons.
- Abyss (noun)
- Meaning: A deep or seemingly bottomless chasm.
- Example: They were lost in the abyss of despair.
- Adulterate (verb)
- Meaning: To make something impure by adding inferior elements.
- Example: The company was fined for adulterating its products with cheap fillers.
- Advocate (verb)
- Meaning: To support or recommend publicly.
- Example: She advocates for better educational policies.
- Aesthetic (adjective)
- Meaning: Concerned with beauty or the appreciation of beauty.
- Example: The aesthetic appeal of the sculpture was undeniable.
- Alacrity (noun)
- Meaning: Brisk and cheerful readiness.
- Example: She accepted the invitation with alacrity.
- Ameliorate (verb)
- Meaning: To make better or more tolerable.
- Example: Measures were taken to ameliorate the suffering of the flood victims.
- Anachronism (noun)
- Meaning: Something out of place in time.
- Example: The presence of a smartphone in the movie set in the 18th century was an anachronism.
- Antipathy (noun)
- Meaning: A deep-seated feeling of dislike.
- Example: His antipathy towards his ex-boss was evident.
- Antithetical (adjective)
- Meaning: Directly opposed or contrasted.
- Example: His views were antithetical to those of his parents.
- Apathy (noun)
- Meaning: Lack of interest, enthusiasm, or concern.
- Example: Voter apathy was high, resulting in low turnout.
- Apocryphal (adjective)
- Meaning: Of doubtful authenticity, although widely circulated as being true.
- Example: The story of the haunted house was apocryphal.
- Arduous (adjective)
- Meaning: Involving or requiring strenuous effort; difficult and tiring.
- Example: Climbing the mountain was an arduous task.
- Assuage (verb)
- Meaning: To make an unpleasant feeling less intense.
- Example: The nurse tried to assuage the patient’s pain.
- Attenuate (verb)
- Meaning: To reduce in force, effect, or value.
- Example: The drug can attenuate the effects of the virus.
- Austere (adjective)
- Meaning: Severe or strict in manner, attitude, or appearance.
- Example: The monk’s austere lifestyle included no luxuries.
- Avarice (noun)
- Meaning: Extreme greed for wealth or material gain.
- Example: His avarice led him to betray his closest friends.
- Banal (adjective)
- Meaning: So lacking in originality as to be obvious and boring.
- Example: The movie was full of banal dialogue.
- Bolster (verb)
- Meaning: To support or strengthen.
- Example: The fall in interest rates is starting to bolster confidence among investors.
- Bombastic (adjective)
- Meaning: High-sounding but with little meaning; inflated.
- Example: The politician’s bombastic speech did not impress the audience.
- Cacophony (noun)
- Meaning: A harsh, discordant mixture of sounds.
- Example: The cacophony of the busy street made it hard to concentrate.
- Candid (adjective)
- Meaning: Truthful and straightforward; frank.
- Example: His candid response was appreciated by the team.
- Capricious (adjective)
- Meaning: Given to sudden and unaccountable changes of mood or behavior.
- Example: His capricious nature made him unreliable.
- Castigate (verb)
- Meaning: To reprimand someone severely.
- Example: The teacher castigated the student for his misbehavior.
- Catalyst (noun)
- Meaning: A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
- Example: The announcement acted as a catalyst for widespread protests.
- Caustic (adjective)
- Meaning: Able to burn or corrode organic tissue by chemical action; sarcastic in a scathing and bitter way.
- Example: His caustic comments hurt her feelings.
- Chicanery (noun)
- Meaning: The use of trickery to achieve a political, financial, or legal purpose.
- Example: The politician’s chicanery won him the election.
- Cogent (adjective)
- Meaning: Clear, logical, and convincing.
- Example: Her cogent argument won over the skeptical audience.
- Contentious (adjective)
- Meaning: Causing or likely to cause an argument; controversial.
- Example: The contentious issue of gun control is often debated.
- Contrite (adjective)
- Meaning: Feeling or expressing remorse or penitence; affected by guilt.
- Example: He was contrite after realizing the impact of his words.
- Convoluted (adjective)
- Meaning: Extremely complex and difficult to follow.
- Example: The novel’s convoluted plot confused many readers.
- Craven (adjective)
- Meaning: Contemptibly lacking in courage; cowardly.
- Example: His craven behavior in the face of danger was disappointing.
- Decorum (noun)
- Meaning: Behavior in keeping with good taste and propriety.
- Example: The queen was known for her decorum and grace.
- Deference (noun)
- Meaning: Humble submission and respect.
- Example: He showed deference to his elders by listening to their advice.
- Deride (verb)
- Meaning: To express contempt for; ridicule.
- Example: The critics derided the new movie as an unoriginal remake.
- Desiccate (verb)
- Meaning: To remove the moisture from something, typically to preserve it.
- Example: The hot sun desiccated the soil, leaving it dry and cracked.
- Desultory (adjective)
- Meaning: Lacking a plan, purpose, or enthusiasm.
- Example: His desultory efforts at studying resulted in poor grades.
- Diatribe (noun)
- Meaning: A forceful and bitter verbal attack against someone or something.
- Example: The politician’s diatribe against his opponent was widely criticized.
- Diffident (adjective)
- Meaning: Modest or shy because of a lack of self-confidence.
- Example: Her diffident manner made it difficult for her to make friends.
- Dilatory (adjective)
- Meaning: Slow to act; intended to cause delay.
- Example: The committee’s dilatory tactics frustrated the members.
- Dilettante (noun)
- Meaning: A person who cultivates an area of interest, such as the arts, without real commitment or knowledge.
- Example: He was a dilettante who enjoyed painting but never pursued it seriously.
- Dirge (noun)
- Meaning: A lament for the dead, especially one forming part of a funeral rite.
- Example: The dirge played at the funeral was very moving.
- Disabuse (verb)
- Meaning: To persuade someone that an idea or belief is mistaken.
- Example: He quickly disabused me of my fanciful notions.
- Disparate (adjective)
- Meaning: Essentially different in kind; not allowing comparison.
- Example: The disparate cultures coexisted peacefully in the city.
- Dissemble (verb)
- Meaning: To conceal one’s true motives, feelings, or beliefs.
- Example: She tried to dissemble her disappointment with a smile.
- Dissonance (noun)
- Meaning: Lack of harmony among musical notes; a tension or clash resulting from the combination of two disharmonious or unsuitable elements.
- Example: The dissonance between the two brothers’ opinions often led to heated arguments.
- Dogmatic (adjective)
- Meaning: Inclined to lay down principles as incontrovertibly true.
- Example: His dogmatic approach to teaching did not allow for any student dissent.
- Dupe (noun)
- Meaning: A person who is easily deceived or tricked.
- Example: He was a dupe, falling for every scam that came his way.
- Eclectic (adjective)
- Meaning: Deriving ideas, style, or taste from a broad and diverse range of sources.
- Example: Her eclectic taste in music included everything from classical to hip-hop.
- Efficacy (noun)
- Meaning: The ability to produce a desired or intended result.
- Example: The efficacy of the new drug was confirmed by clinical trials.
- Elegy (noun)
- Meaning: A poem of serious reflection, typically a lament for the dead.
- Example: The poet wrote an elegy in memory of his late friend.
- Eloquent (adjective)
- Meaning: Fluent or persuasive in speaking or writing.
- Example: His eloquent speech captivated the audience.
- Emulate (verb)
- Meaning: To match or surpass, typically by imitation.
- Example: She hoped to emulate her mother’s success as a lawyer.
- Enervate (verb)
- Meaning: To cause someone to feel drained of energy or vitality; weaken.
- Example: The hot sun enervated the marathon runners.
- Engender (verb)
- Meaning: To cause or give rise to a feeling, situation, or condition.
- Example: The new policy engendered considerable debate among the students.
- Ephemeral (adjective)
- Meaning: Lasting for a very short time.
- Example: The beauty of the cherry blossoms is ephemeral, disappearing within a week.
- Equivocate (verb)
- Meaning: To use ambiguous language so as to conceal the truth or avoid committing oneself.
- Example: The politician equivocated when asked about his stance on healthcare.
- Erudite (adjective)
- Meaning: Having or showing great knowledge or learning.
- Example: The professor’s erudite lecture on quantum physics impressed the students.
- Esoteric (adjective)
- Meaning: Intended for or likely to be understood by only a small number of people with a specialized knowledge or interest.
- Example: The author’s esoteric writing style was difficult for the average reader to understand.
- Eulogy (noun)
- Meaning: A speech or piece of writing that praises someone or something highly, typically someone who has just died.
- Example: His best friend gave a moving eulogy at the funeral.
- Euphemism (noun)
- Meaning: A mild or indirect word or expression substituted for one considered to be too harsh or blunt when referring to something unpleasant or embarrassing.
- Example: “Passed away” is a common euphemism for “died.”
- Exacerbate (verb)
- Meaning: To make a problem, bad situation, or negative feeling worse.
- Example: The new law only exacerbated the problem of illegal immigration.
- Exculpate (verb)
- Meaning: To show or declare that someone is not guilty of wrongdoing.
- Example: The evidence presented in court exculpated the defendant.
- Exigent (adjective)
- Meaning: Pressing; demanding.
- Example: The exigent demands of her job left her with little free time.
- Exonerate (verb)
- Meaning: To absolve someone from blame for a fault or wrongdoing.
- Example: The DNA evidence exonerated the suspect.
- Facetious (adjective)
- Meaning: Treating serious issues with deliberately inappropriate humor.
- Example: His facetious remarks during the meeting were not appreciated.
- Fervid (adjective)
- Meaning: Intensely enthusiastic or passionate.
- Example: The fervid speech of the politician stirred the crowd.
- Florid (adjective)
- Meaning: Having a red or flushed complexion; elaborately or excessively intricate or complicated.
- Example: His florid face showed signs of embarrassment.
- Foment (verb)
- Meaning: To instigate or stir up an undesirable or violent sentiment or course of action.
- Example: The rebels tried to foment a revolution.
- Frugality (noun)
- Meaning: The quality of being economical with money or food; thriftiness.
- Example: Her frugality allowed her to save a significant amount of money.
- Garrulous (adjective)
- Meaning: Excessively talkative, especially on trivial matters.
- Example: The garrulous old man could talk for hours about his youth.
- Gregarious (adjective)
- Meaning: Fond of company; sociable.
- Example: She was a gregarious person who loved hosting parties.
- Guile (noun)
- Meaning: Sly or cunning intelligence.
- Example: He used his guile to escape from the tricky situation.
- Harangue (noun)
- Meaning: A lengthy and aggressive speech.
- Example: The activist delivered a harangue against the government’s policies.
- Homogenous (adjective)
- Meaning: Of the same kind; alike.
- Example: The town had a homogenous population with little diversity.
- Iconoclast (noun)
- Meaning: A person who attacks or criticizes cherished beliefs or institutions.
- Example: The artist was an iconoclast who challenged traditional views.
- Imperturbable (adjective)
- Meaning: Unable to be upset or excited; calm.
- Example: His imperturbable demeanor reassured everyone during the crisis.
- Implacable (adjective)
- Meaning: Unable to be placated; relentless.
- Example: The implacable advance of the enemy forces left the villagers in fear.
- Inchoate (adjective)
- Meaning: Just begun and so not fully formed or developed; rudimentary.
- Example: The new administration’s policies are still inchoate.
- Ingenious (adjective)
- Meaning: Clever, original, and inventive.
- Example: Her ingenious solution to the problem won her the competition.
- Inimical (adjective)
- Meaning: Tending to obstruct or harm.
- Example: The policy changes were inimical to the interests of the workers.
- Innocuous (adjective)
- Meaning: Not harmful or offensive.
- Example: His comments were innocuous, but she took offense anyway.
- Insipid (adjective)
- Meaning: Lacking flavor; dull; not at all stimulating.
- Example: The soup was insipid and needed more seasoning.
- Intransigent (adjective)
- Meaning: Unwilling or refusing to change one’s views or to agree about something.
- Example: The union’s intransigent stance on the contract led to a prolonged strike.
- Intrepid (adjective)
- Meaning: Fearless; adventurous (often used for rhetorical or humorous effect).
- Example: The intrepid explorer ventured into the uncharted territory.
- Inundate (verb)
- Meaning: To overwhelm with things or people to be dealt with; flood.
- Example: The office was inundated with calls from concerned citizens.
- Irascible (adjective)
- Meaning: Having or showing a tendency to be easily angered.
- Example: His irascible temperament made him difficult to work with.
- Laconic (adjective)
- Meaning: Using very few words.
- Example: His laconic reply suggested a lack of interest in the topic.
- Lament (verb)
- Meaning: To express passionate grief about.
- Example: She lamented the loss of her best friend.
- Lethargic (adjective)
- Meaning: Affected by lethargy; sluggish and apathetic.
- Example: After the long flight, she felt too lethargic to do anything.
- Loquacious (adjective)
- Meaning: Tending to talk a great deal; talkative.
- Example: The loquacious host kept the guests entertained all night.
- Lethargic (adjective)
- Meaning: Affected by lethargy; sluggish and apathetic.
- Example: After the long flight, she felt too lethargic to do anything.
- Loquacious (adjective)
- Meaning: Tending to talk a great deal; talkative.
- Example: The loquacious host kept the guests entertained all night.
- Lucid (adjective)
- Meaning: Expressed clearly; easy to understand.
- Example: His explanation was lucid and to the point.
- Magnanimous (adjective)
- Meaning: Generous or forgiving, especially toward a rival or less powerful person.
- Example: The magnanimous winner shared the prize money with his competitors.
- Malleable (adjective)
- Meaning: Easily influenced; pliable.
- Example: The malleable mind of the young child was easily shaped by his teachers.
- Misanthrope (noun)
- Meaning: A person who dislikes humankind and avoids human society.
- Example: The old man was a misanthrope who lived alone in the woods.
- Mitigate (verb)
- Meaning: To make less severe, serious, or painful.
- Example: Measures were taken to mitigate the impact of the economic downturn.
- Obdurate (adjective)
- Meaning: Stubbornly refusing to change one’s opinion or course of action.
- Example: Despite the evidence, he remained obdurate and would not admit he was wrong.
- Obfuscate (verb)
- Meaning: To render obscure, unclear, or unintelligible.
- Example: The politician’s explanations only served to obfuscate the issue further.
- Obsequious (adjective) – Meaning: Obedient or attentive to an excessive or servile degree. – Example: The obsequious assistant complied with every request of his boss, no matter how trivial.
- Occlude (verb) – Meaning: To stop, close up, or obstruct. – Example: The pipe was occluded by a large piece of debris.
- Opprobrium (noun) – Meaning: Harsh criticism or censure. – Example: The government faced opprobrium for its handling of the crisis.
- Paradox (noun) – Meaning: A seemingly absurd or self-contradictory statement or proposition that when investigated or explained may prove to be well founded or true. – Example: The paradox of her situation was that she had so much but felt so empty.
- Paragon (noun) – Meaning: A person or thing regarded as a perfect example of a particular quality. – Example: He was considered a paragon of virtue.
- Pedant (noun) – Meaning: A person who is excessively concerned with minor details and rules or with displaying academic learning. – Example: The professor was a pedant who could not see the forest for the trees.
- Perfidious (adjective) – Meaning: Deceitful and untrustworthy. – Example: The perfidious actions of the spy were uncovered.
- Perfunctory (adjective) – Meaning: Carried out with a minimum of effort or reflection. – Example: His perfunctory response indicated a lack of interest.
- Permeate (verb) – Meaning: To spread throughout something; pervade. – Example: The smell of fresh bread permeated the house.
- Placate (verb) – Meaning: To make someone less angry or hostile. – Example: He tried to placate his angry boss with a sincere apology.
- Plastic (adjective) – Meaning: Easily shaped or molded. – Example: The artist used a plastic material to create the sculpture.
- Plethora (noun) – Meaning: A large or excessive amount of something. – Example: There was a plethora of food at the banquet.
- Pragmatic (adjective) – Meaning: Dealing with things sensibly and realistically in a way that is based on practical rather than theoretical considerations. – Example: Her pragmatic approach to problem-solving was highly effective.
- Precipitate (verb) – Meaning: To cause something to happen suddenly or unexpectedly. – Example: The crisis was precipitated by a sudden drop in oil prices.
- Prevaricate (verb) – Meaning: To speak or act in an evasive way. – Example: When asked about his involvement, he began to prevaricate.
- Proclivity (noun) – Meaning: A tendency to choose or do something regularly; an inclination or predisposition toward a particular thing. – Example: She has a proclivity for hard work.
- Prodigal (adjective) – Meaning: Spending money or resources freely and recklessly; wastefully extravagant. – Example: The prodigal son returned home after wasting his inheritance.
- Propitiate (verb) – Meaning: To win or regain the favor of a god, spirit, or person by doing something that pleases them. – Example: They offered sacrifices to propitiate the gods.
- Propriety (noun) – Meaning: The state or quality of conforming to conventionally accepted standards of behavior or morals. – Example: She behaved with utmost propriety at the formal event.
- Quotidian (adjective) – Meaning: Of or occurring every day; daily. – Example: The quotidian tasks of life can sometimes feel mundane.
- Repudiate (verb) – Meaning: To refuse to accept or be associated with. – Example: The company repudiated claims that it had acted irresponsibly.
- Reticent (adjective) – Meaning: Not revealing one’s thoughts or feelings readily. – Example: She was reticent about her personal life.
- Soporific (adjective) – Meaning: Tending to induce drowsiness or sleep. – Example: The professor’s soporific lecture put half the class to sleep.
- Specious (adjective) – Meaning: Superficially plausible, but actually wrong. – Example: His argument was specious and failed to convince the jury.
- Spurious (adjective) – Meaning: Not being what it purports to be; false or fake. – Example: The spurious claims of the advertisement misled many customers.
- Stolid (adjective) – Meaning: Calm, dependable, and showing little emotion or animation. – Example: His stolid demeanor made it difficult to gauge his reaction.
- Sublime (adjective) – Meaning: Of such excellence, grandeur, or beauty as to inspire great admiration or awe. – Example: The view from the mountaintop was sublime.
- Tacit (adjective) – Meaning: Understood or implied without being stated. – Example: There was a tacit agreement between the two friends.
- Taciturn (adjective) – Meaning: Reserved or uncommunicative in speech; saying little. – Example: The taciturn boy kept to himself at the party.
- Tirade (noun) – Meaning: A long, angry speech of criticism or accusation. – Example: The manager’s tirade left the employees feeling demoralized.
- Torpid (adjective) – Meaning: Mentally or physically inactive; lethargic. – Example: The heat made everyone torpid and uninterested in work.
- Tortuous (adjective) – Meaning: Full of twists and turns. – Example: The tortuous road up the mountain was difficult to navigate.
GMAT Vocabulary List | Image


Why Not Just Memorize a List?
The GMAT doesn’t test vocabulary directly. Focusing solely on memorizing a long list might be a waste of time. Here’s why:
- Limited Focus: The GMAT tests your ability to understand context, not just isolated word definitions.
- Time Drain: Memorizing hundreds of words is inefficient and stressful. There’s a smarter way!
The GMAT is a test of reasoning, not a vocabulary spelling bee. By focusing on understanding context clues, root words, and synonyms, you’ll develop the skills needed to tackle GMAT vocabulary with confidence. Now go forth and conquer that test!