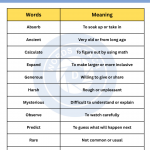
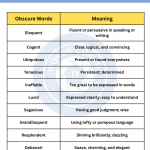
Transition Phrases
Have you ever read a piece of writing that feels like a bumpy ride? Sentences seem disconnected, and ideas jump around without a clear path. This is often the result of missing transition phrases.
These little words and phrases are the glue that holds your writing together. They act like bridges, smoothly connecting your sentences and guiding your reader through your thoughts. Strong transitions create a clear flow, making your writing easier to understand and follow.
Why Use Transition Phrases?
Here are some compelling reasons to embrace transition phrases:
- Improved Clarity: Transitions help readers see the relationships between ideas. They understand how each sentence builds upon the previous one, creating a cohesive whole.
- Enhanced Flow: Transitions create a smooth reading experience. Without them, your writing can feel choppy and disjointed, leaving your reader lost in a maze of information.
- Stronger Arguments: Transitions help you build a logical case. By highlighting cause-and-effect relationships or contrasting viewpoints, transitions strengthen your argument’s persuasiveness.
Here’s a list of transition phrases categorized by their function:
To Add Information:
Additionally
Meaning: This transition phrase is used to introduce an additional point or idea that supports the previous one.
Examples:
- John enjoys playing basketball. Additionally, he is a talented pianist.
- The company experienced a surge in profits last quarter. Additionally, they expanded their operations to international markets.
Furthermore
Meaning: Furthermore is used to add more information or evidence to strengthen the previous point.
Examples:
- Sarah is an excellent writer. Furthermore, she has won several awards for her poetry.
- The research indicates a significant decrease in pollution levels. Furthermore, public awareness campaigns have contributed to this positive change.
Moreover
Meaning: Moreover is similar to ‘furthermore’ and is used to emphasize the importance or relevance of the additional information being provided.
Examples:
- The new software improves efficiency and reduces costs. Moreover, it enhances data security, which is crucial for our organization.
- The study found a correlation between exercise and mental well-being. Moreover, it suggests that regular physical activity can reduce stress levels.
In addition
Meaning: This phrase is used to introduce another point that adds to the previous one, often in a more formal context.
Examples:
- The company offers competitive salaries and benefits. In addition, employees have access to professional development opportunities.
- The museum features an impressive collection of modern art. In addition, it hosts regular exhibitions showcasing emerging artists.
Also
Meaning: Also is a simple transition phrase that is used to add another point or idea to the discussion.
Examples:
- Jane enjoys hiking and photography. Also, she volunteers at the local animal shelter.
- The new restaurant specializes in Italian cuisine. Also, it offers a selection of fine wines and desserts.
Likewise
Meaning: Likewise is used to indicate that a similar point or idea is being presented.
Examples:
- Sarah enjoys reading classic literature. Likewise, she appreciates watching old movies from the same era.
- The company prioritizes customer satisfaction. Likewise, it values employee feedback and engagement.
Besides
Meaning: Besides is used to introduce an additional point or reason that is different from the ones already mentioned.
Examples:
- Besides being an accomplished musician, Tom is also a skilled painter.
- Besides the beautiful scenery, the town offers excellent hiking trails and outdoor activities.
Not only…but also
Meaning: This structure is used to emphasize two related ideas or qualities, indicating that both are significant.
Examples:
- Not only does the new software improve productivity, but it also enhances collaboration among team members.
- The conference attracted not only experts in the field but also students and enthusiasts eager to learn more.
To Show Contrast:
However
Meaning: This transition phrase is used to introduce a contrasting or conflicting idea to the one previously mentioned.
Examples:
- The weather forecast predicted rain; however, the skies remained clear throughout the day.
- The project was challenging; however, the team managed to complete it ahead of schedule.
On the other hand
Meaning: On the other hand introduces an alternative perspective or contrasting viewpoint to the one just discussed.
Examples:
- Some people prefer to work in an office environment. On the other hand, others thrive in remote settings.
- Exercise is crucial for maintaining physical health. On the other hand, mental well-being also requires adequate rest and relaxation.
Conversely
Meaning: Conversely is used to present an idea that is opposite or contrary to the previous one.
Examples:
- While some people enjoy the hustle and bustle of city life, others prefer the tranquility of rural areas. Conversely, some find rural life isolating.
- Higher education often leads to better career opportunities. Conversely, it can also result in significant student debt.
Nevertheless
Meaning: Nevertheless is used to indicate that despite the previous statement or circumstances, the following point remains true or relevant.
Examples:
- The weather was chilly; nevertheless, they decided to go for a hike in the mountains.
- The project faced numerous challenges; nevertheless, the team persevered and achieved success.
Nonetheless
Meaning: Similar to nevertheless, nonetheless signifies that the upcoming point is true despite what has been said or done before.
Examples:
- The restaurant received mixed reviews; nonetheless, it remained popular among locals and tourists alike.
- The economy experienced a downturn; nonetheless, certain sectors continued to thrive.
In contrast
Meaning: In contrast is used to highlight differences between two or more things or ideas.
Examples:
- The coastal region is known for its mild climate and sandy beaches. In contrast, the mountainous area experiences colder temperatures and heavy snowfall.
- Traditional teaching methods rely heavily on lectures and textbooks. In contrast, experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and real-world applications.
While
Meaning: While is used to introduce a contrasting or conflicting idea to the one presented in the previous clause.
Examples:
- While some people prefer coffee, others opt for tea as their morning beverage.
- While technology has revolutionized communication, it has also led to concerns about privacy and security.
Although
Meaning: Although introduces a concession or contrasting idea to the main point of the sentence.
Examples:
- Although it was raining, they decided to proceed with the outdoor event.
- Although she was tired, she stayed up late to finish her assignment.
Yet
Meaning: Yet is used to introduce a contrasting idea or outcome despite what has been mentioned previously.
Examples:
- The team faced numerous setbacks; yet, they emerged victorious in the end.
- The movie received mixed reviews; yet, it became a box office success.
Instead
Meaning: Instead indicates a preference for one option or course of action over another.
Examples:
- Instead of driving, they opted to take the train for a more scenic journey.
- Instead of ordering takeout, they decided to cook dinner at home.
To Provide Examples:
For example
Meaning: This transition phrase is used to introduce a specific example that illustrates or supports the preceding statement.
Example: Many fruits are rich in vitamin C. For example, oranges, strawberries, and kiwis are excellent sources of this essential nutrient.
For instance
Meaning: Similar to “for example,” “for instance” is used to introduce a specific case or example to further illustrate the point.
Example: Various forms of exercise can improve cardiovascular health. For instance, running, swimming, and cycling are all effective aerobic activities.
Such as
Meaning: “Such as” is used to introduce examples or instances that exemplify a broader category or concept.
Example: Many countries in Asia have diverse culinary traditions. Dishes such as sushi in Japan, pad thai in Thailand, and kimchi in Korea showcase the region’s rich culinary heritage.
Namely
Meaning: Namely is used to introduce specific items or examples within a broader category or list.
Example: The company offers various employee benefits, namely, health insurance, retirement plans, and flexible work schedules.
In particular
Meaning: This transition phrase is used to emphasize a specific aspect or detail within a broader context.
Example: The research study focused on the effects of stress on mental health. In particular, it examined the relationship between workplace stress and anxiety disorders.
To illustrate
Meaning: “To illustrate” is used to introduce an example or scenario that helps clarify or demonstrate the point being made.
Example: Learning a new language can be challenging. To illustrate, imagine trying to communicate in a foreign country without knowing the local language.

To Emphasize:
Indeed
Meaning: “Indeed” is used to emphasize a point or to confirm that something is true.
Example: The results of the experiment were consistent with our hypothesis. Indeed, the data supported our initial assumptions.
Certainly
Meaning: “Certainly” is used to express agreement or to affirm a statement.
Example: The new regulations will have a significant impact on the industry. Certainly, companies will need to adapt to these changes.
Undoubtedly
Meaning: “Undoubtedly” indicates that something is unquestionably true or certain.
Example: The team’s hard work and dedication undoubtedly contributed to their success in the competition.
Without a doubt
Meaning: Similar to “undoubtedly,” “without a doubt” expresses absolute certainty or conviction.
Example: His years of experience and expertise in the field make him, without a doubt, the best candidate for the job.
Above all
Meaning: “Above all” is used to emphasize the most important aspect or consideration.
Example: In a fast-paced industry, customer satisfaction should be the priority above all.
Especially
Meaning: “Especially” is used to single out a particular case or circumstance among others.
Example: She enjoys outdoor activities, especially hiking and camping in the mountains.
Particularly
Meaning: “Particularly” is used to highlight a specific aspect or detail within a broader context.
Example: The conference focused on various topics related to sustainability, particularly renewable energy sources.
In fact
Meaning: “In fact” is used to introduce a statement that provides additional information or confirms something previously mentioned.
Example: Many people believe that technology has made us more connected. In fact, studies show that excessive screen time can lead to feelings of isolation.
To Show Cause and Effect:
Therefore
Meaning: “Therefore” is used to indicate a logical consequence or conclusion based on the preceding information.
Example: The experiment yielded consistent results; therefore, we can conclude that the hypothesis is valid.
Thus
Meaning: “Thus” is used to introduce a result or conclusion that follows logically from the preceding statement or argument.
Example: Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health. Thus, incorporating physical activity into your daily routine is essential for overall well-being.
Consequently
Meaning: “Consequently” signifies that a particular event or circumstance is the direct result of something else.
Example: The company implemented cost-cutting measures; consequently, several employees were laid off.
As a result
Meaning: “As a result” is used to indicate the consequence or outcome of a preceding action or event.
Example: The team worked diligently to meet the project deadline. As a result, they delivered the final product ahead of schedule.
Hence
Meaning: “Hence” is used to indicate the reason or cause for something, often in a formal or academic context.
Example: The roads were closed due to heavy snowfall; hence, commuters were advised to use alternative routes.
Accordingly
Meaning: “Accordingly” is used to indicate that a particular action or decision is appropriate or in line with previous information or circumstances.
Example: The company experienced a surge in demand for its products. Accordingly, they ramped up production to meet customer needs.
Due to
Meaning: “Due to” is used to indicate the cause or reason for something.
Example: The event was canceled due to inclement weather conditions.
Because
Meaning: “Because” is used to introduce the reason or cause for something.
Example: She couldn’t attend the meeting because she was feeling unwell.
Since
Meaning: “Since” is used to introduce a reason or explanation for something, often in relation to time or causality.
Example: Since the restaurant opened, it has become a popular dining destination in the city.
To Summarize or Conclude:
In conclusion
Meaning: “In conclusion” is used to signal the final remarks or thoughts in a piece of writing or speech.
Example: In conclusion, it is evident that technology has revolutionized various aspects of modern life.
To sum up
Meaning: “To sum up” is used to provide a concise overview or summary of the main points discussed.
Example: To sum up, effective communication skills are essential for building strong relationships in both personal and professional settings.
Ultimately
Meaning: “Ultimately” is used to emphasize the most important point or outcome.
Example: Ultimately, the success of the project depends on effective collaboration and communication among team members.
All in all
Meaning: “All in all” is used to provide a comprehensive evaluation or assessment of a situation or topic.
Example: All in all, the event was a resounding success, thanks to the dedication and hard work of everyone involved.
In summary
Meaning: “In summary” is used to encapsulate the main points or arguments discussed in a concise manner.
Example: In summary, the research findings suggest a strong correlation between regular exercise and improved mental health.
To conclude
Meaning: “To conclude” signals the final part of a discussion or presentation.
Example: To conclude, it is crucial for policymakers to consider the long-term environmental impact of their decisions.
On the whole
Meaning: “On the whole” is used to provide a general assessment or overview of a situation or topic.
Example: On the whole, the company’s financial performance has been satisfactory despite the challenges faced in the market.
To summarize
Meaning: “To summarize” is used to succinctly restate the main points or arguments.
Example: To summarize, effective time management skills are essential for achieving productivity and success in both personal and professional endeavors.
To Sequence Ideas:
First(ly)
Meaning: “First(ly)” is used to introduce the initial point or idea in a sequence.
Example: First, we need to gather all the necessary materials before we can start the experiment.
Second(ly)
Meaning: “Second(ly)” follows the introduction of the first point and introduces the next idea in the sequence.
Example: Secondly, we must carefully calibrate the instruments to ensure accurate measurements.
Next
Meaning: “Next” indicates the idea or action that follows the current one in a chronological or logical sequence.
Example: We need to mix the ingredients thoroughly. Next, we’ll pour the mixture into the baking pan.
Then
Meaning: “Then” is used to indicate the action or event that occurs after the previous one.
Example: We need to let the dough rise for an hour. Then, we can proceed with baking it in the oven.
Afterward
Meaning: “Afterward” refers to the action or event that occurs following another event or action.
Example: We completed the first phase of the project. Afterward, we began working on the second phase.
Subsequently
Meaning: “Subsequently” indicates that an action or event follows another one in sequence.
Example: The team implemented the new software system. Subsequently, productivity levels increased across the organization.
Finally
Meaning: “Finally” marks the last point or idea in a sequence or the ultimate conclusion.
Example: Finally, we presented our findings to the board of directors and received their approval to proceed with the project.
Meanwhile
Meaning: “Meanwhile” is used to indicate that something is happening at the same time as something else.
Example: We continued with our research. Meanwhile, our competitors were launching their own products into the market.
Simultaneously
Meaning: “Simultaneously” indicates that two or more actions or events are occurring at the same time.
Example: The team members were working simultaneously on different aspects of the project to meet the deadline.
To Provide Clarification:
In other words
Meaning: “In other words” is used to express something in a different way or to rephrase a statement to make it clearer.
Example: The project requires a significant investment of time and resources. In other words, it will demand a substantial commitment from the team.
That is to say
Meaning: “That is to say” is used to explain or clarify something in a different manner.
Example: The company aims to expand its market presence through strategic partnerships. That is to say, it plans to collaborate with key industry players to achieve its goals.
To clarify
Meaning: “To clarify” is used to provide additional information or to make a point more understandable.
Example: The new policy aims to streamline procedures and improve efficiency. To clarify, employees will undergo training to familiarize themselves with the updated guidelines.
Put another way
Meaning: “Put another way” is used to restate an idea or concept using different words.
Example: The study suggests that regular exercise can improve cognitive function and memory. Put another way, staying physically active can enhance brain health and cognitive abilities.
In simpler terms
Meaning: “In simpler terms” is used to explain a complex idea or concept in a more straightforward manner.
Example: The theory proposes a multi-dimensional approach to understanding human behavior. In simpler terms, it suggests that behavior is influenced by various internal and external factors.
To Introduce a Comparison:
Similarly
Meaning: “Similarly” is used to indicate that something is alike or comparable to something else.
Example: Cats are known for their agility and independence. Similarly, many people admire the resilience and self-reliance of wild animals.
Likewise
Meaning: “Likewise” is used to express that the same action or quality applies to another person or thing.
Example: Sarah enjoys hiking and exploring nature. Likewise, her brother shares her passion for outdoor activities.
In comparison
Meaning: “In comparison” is used to contrast two or more items or ideas to show their similarities or differences.
Example: In comparison to traditional classrooms, online learning offers greater flexibility and accessibility for students of all ages.
Just as
Meaning: “Just as” is used to draw a comparison between two similar actions or situations.
Example: Just as plants require sunlight to grow, humans need nourishment and care to thrive physically and emotionally.
To Provide Time Reference:
Meanwhile
Meaning: “Meanwhile” is used to indicate events happening at the same time as another event.
Example: John was busy preparing dinner. Meanwhile, Sarah was setting the table in the dining room.
Simultaneously
Meaning: “Simultaneously” is used to describe actions or events occurring at the same time.
Example: The dancers moved gracefully across the stage, while the musicians played the accompanying music simultaneously.
Subsequently
Meaning: “Subsequently” is used to show that one event follows another in chronological order.
Example: The team completed the first phase of the project successfully. Subsequently, they began working on the next stage.
Finally
Meaning: “Finally” is used to indicate the last point, action, or event in a sequence.
Example: After weeks of rehearsals, the play finally premiered to an enthusiastic audience.
Later
Meaning: “Later” is used to describe events occurring at a time subsequent to the present or an earlier time.
Example: Sarah met with her colleagues in the morning. Later, she attended a client meeting in the afternoon.
Afterward
Meaning: “Afterward” is used to indicate that an action or event occurs following another action or event.
Example: The students completed their exams in the morning. Afterward, they celebrated the end of the semester with a party.
Before
Meaning: “Before” is used to indicate that an action or event occurs prior to another action or event.
Example: The guests arrived at the party before the host had finished preparing the food.
Contrast Transition Words Exercise
Using transition phrases effectively can enhance the readability and coherence of your writing, making it easier for your audience to follow your ideas and arguments.